
Introduction to GMP

The Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) specifies the mandatory requirements for the rationality of the production process, the suitability of the production equipment and the accuracy and standardization of the production operations. The latest version of the "Good Manufacturing Practice (2010 Revision)", which was deliberated and adopted at the Executive Meeting of the Ministry of Health on October 19, 2010, is hereby promulgated and shall come into force as of March 1, 2011.
GMP is a basic guideline for drug production and quality management, which applies to the whole process of drug preparation production and the key processes affecting the quality of finished products in API production. Vigorous implementation of drug GMP is an important measure to improve drugs' quality and to avoid contamination and cross-contamination during drug production, thus minimizing the occurrence of errors.
Currently, the global distribution of drugs manufactured in China requires manufacturers to comply not only with the GMP (2010 revision) regulations in China, but also with the international standards of EU/GMP and FDA-cGMP.
The GMP does not detail the requirements for the design, construction, and testing of biological cleanrooms. For more details, please refer to the relevant GMP implementation guidelines, drug GMP certification inspection and evaluation standards, FED 209E, ISO14644, ISO14698, IEST, international GB/T, EN1822 and other standards.
Cleanrooms and contamination control technologies are some of the main tools used to ensure the successful implementation of GMP
Standards for biological cleanrooms
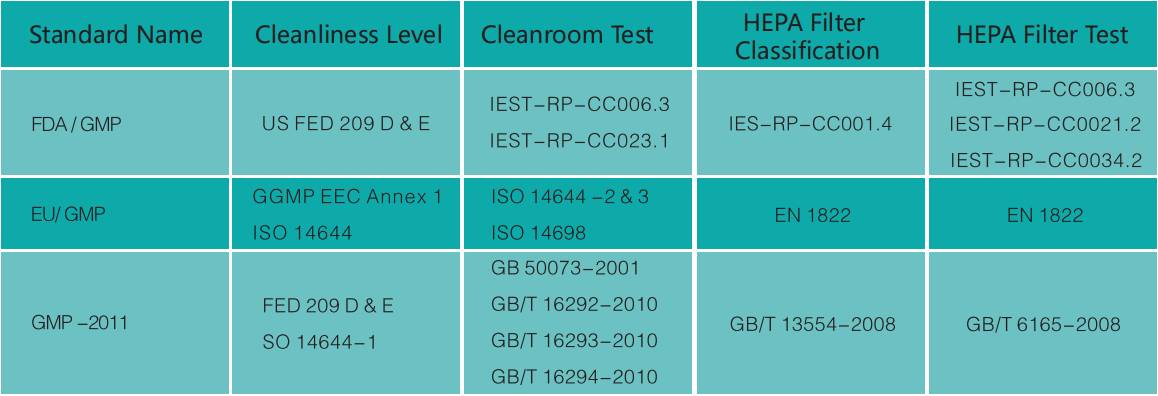
Standards for biological cleanrooms
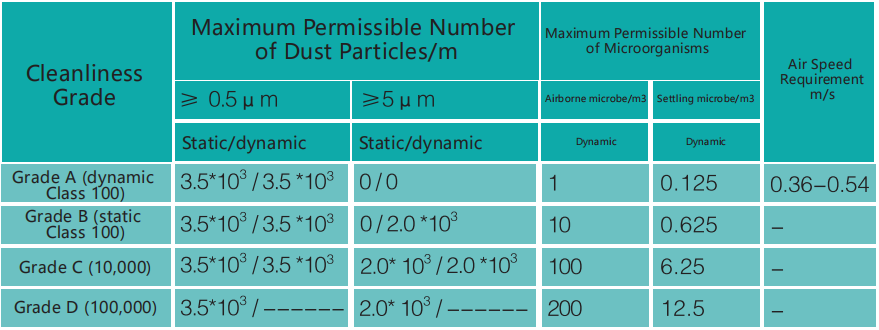
The air clean zone of biological cleanroom is divided into four zones:
Grade A: High risk operation zones, i.e. zones that directly affect operations, such as tunnel sterilization oven, aseptic filling, bottle opening, autoclave cooling area. These zones require Class 100 laminar flow and directly affect the product quality.
Grade B: Zones that indirectly affect the aseptic operations and directly surround the Grade A zones, such as aseptic filling room and autoclave cooling room.
Grade C and D: Transitional clean zones before entering the sterile production area, such as preparation room, dressing room and buffer room.
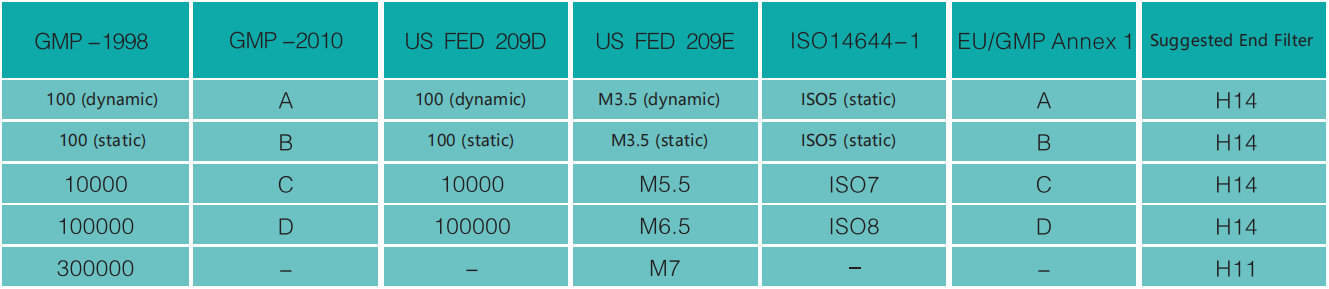
General comparison of different standards for suspended particle classification in GMP
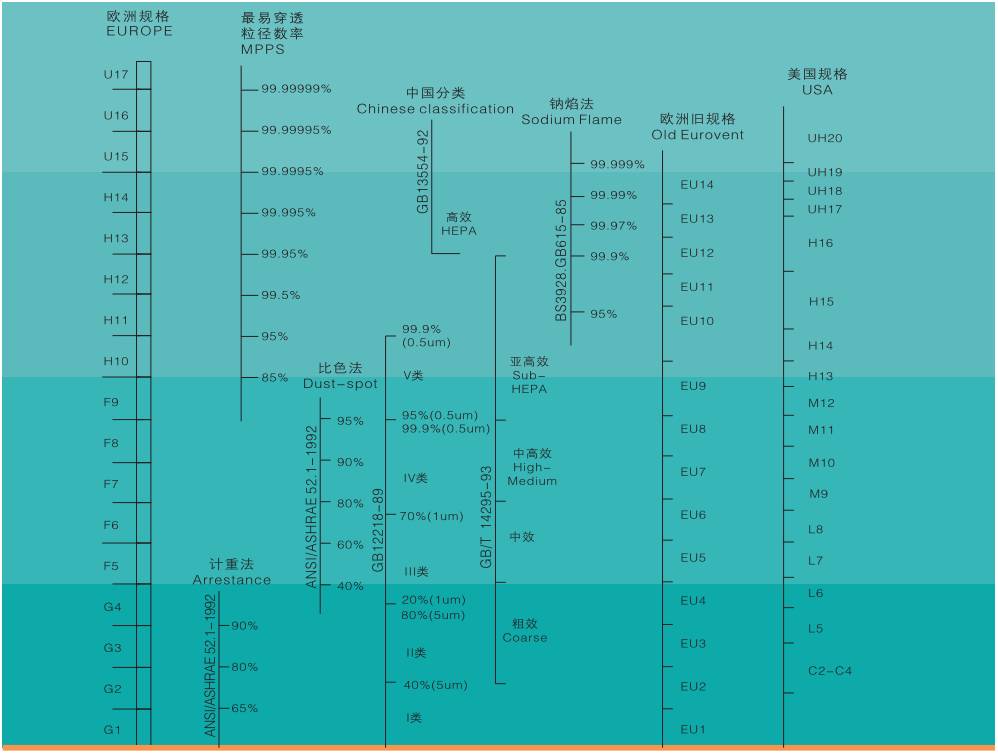
Comparison of air filter efficiency specifications
Consultation